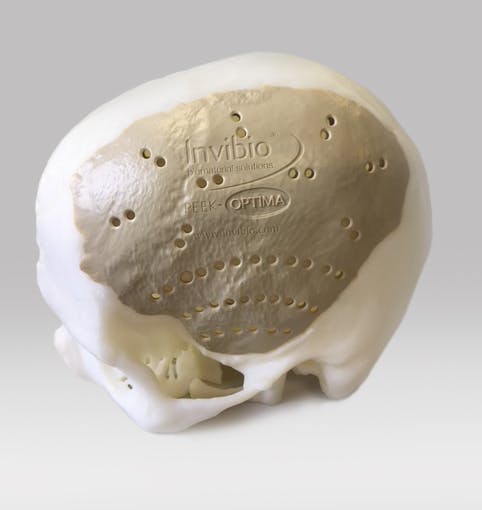
Why PEEK is an Excellent Solution for CMF Implants
Permanent, low profile PEEK solutions for craniomaxillofacial surgery reconstructions
2.3 times higher brain function score with PEEK compared with Titanium1
Why PEEK is an Excellent Solution for CMF Implants
Permanent, low profile PEEK solutions for craniomaxillofacial surgery reconstructions
2.3 times higher brain function score with PEEK compared with Titanium1


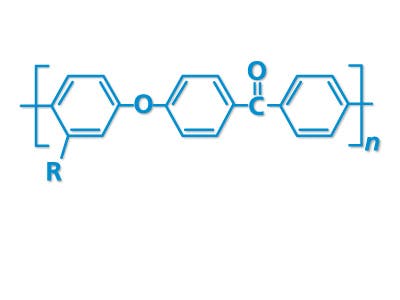
PEEK-OPTIMATM high performance polymer is a strong, permanent, functional alternative to traditional structural materials like metal that can be used to manufacture custom cranial implants. PEEK-OPTIMA’s biomechanical properties are similar to bone, result in better clinical outcomes and have improved cosmetic satisfaction compared to titanium1-9.

Invibio launches PEEK-OPTIMA™ AM filament, making available the trusted implantable-grade polymer in a form specifically developed for Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) additive manufacturing processes.

Collaboration with Bond3D to develop implants of the future
Ready to start a PEEK project?
Tell us more about your next CMF project, and one of our PEEK experts will be in touch with more information about how we can support you
References
1. Zhang Q, Yuan Y, Li X, et al. A Large Multicenter Retrospective Research on Embedded Cranioplasty and Covered Cranioplasty. World Neurosurg. 2018;112:e645-e651.
2. Jack Henry, Michael Amoo, Joseph Taylor, David P.O'Brien, MMedSc, Complications of Cranioplasty in Relation to Material: Systematic Review, Network Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression, Neurosurgery 89:383–394, 2021.
3. Yirui Sun, Yue Hu, et al. Association between metal hypersensitivity and implant failure in patient who underwent titanium cranioplasty, J Neurosurg July6, 2018
4. Lethaus B, Bloebaum M, Koper D, Poort-Ter Laak M, Kessler P. Interval cranioplasty with patient-specific implants and autogenous bone grafts-success and cost analysis. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014;42(8):1948-1951.
5. Punchak M, Chung LK, Lagman C, et al. Outcomes following polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cranioplasty: Systematic review and meta analysis. J Clin Neurosci. 2017;41:30-35.
6. Camarini ET, Tomeh JK, Dias RR, et al. Reconstruction of frontal bone using specific implant polyether-ether-ketone. J Craniofac Surg 2011;22:2205-7
7. Rho, JY et al (1993). “Young’s modulus of trabecular and cortical bone material: Ultrasonic and microtensile measurements”. Journal of Biomechanics 26 (2); 111–119
8. Victrex property guide.
9. Jalbert F, Boetto S, Nadon F, Lauwers F, Schmidt E, Lopez R. One-step primary reconstruction for complex craniofacial resection with PEEK custom-made implants. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014;42(2):141-148.
*non-metal – PEEK is a polymer containing metal ions at levels below ppb
Pouya Nezafati, et al. ZipFix Versus Conventional Sternal Closure: One-Year Follow-Up. Heart Lung Circ. 2019 Mar;28(3):443-449.
10. Ludovic Melly, et al. A new cable-tie-based sternal closure device: infectious considerations. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2013 Aug;17(2):219-23.
11. Martin TR Grapow, et al. A new cable-tie based sternal closure system: description of the device, technique of implantation and first clinical evaluation. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012 Jun 25;7:59.
12. Kazuma Takashima, et al. A carbon fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone intramedullary nail improves fracture site visibility on postoperative radiographic images. Injury. 2021 Aug;52(8):2225-2232.
13. Images courtesy of Able Medical Devices. ValkyrieTM is a registered trademark of Able Medical Devices Inc.
14. Images courtesy of Neos Surgery. CranialLoopTM and SternfixTM are registered trademarks of Neos Surgery SL
15. Pouya Nezafati, et al. ZipFix Versus Conventional Sternal Closure: One-Year Follow-Up. Heart Lung Circ. 2019 Mar;28(3):443-449.
16. Ludovic Melly, et al. A new cable-tie-based sternal closure device: infectious considerations. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2013 Aug;17(2):219-23.
17. Martin TR Grapow, et al. A new cable-tie based sternal closure system: description of the device, technique of implantation and first clinical evaluation. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012 Jun 25;7:59.
18. Kazuma Takashima, et al. A carbon fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone intramedullary nail improves fracture site visibility on postoperative radiographic images. Injury. 2021 Aug;52(8):2225-2232.

From the invention of PEEK over 40 years ago, Victrex has continually pioneered new PAEK-based polymers, materials and solutions that have transformed markets, delivering global impact in the toughest environments.
We bring transformational & sustainable solutions that address world material challenges every day.